Build MCP Servers in Minutes: 5 Easy Steps with FastMCP in Python
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a powerful standard for connecting Large Language Models (LLMs) to external data and tools, acting like a universal bridge for AI interactions. If you're a Python developer looking to enhance your AI workflows, FastMCP is the go-to library to simplify building MCP servers. In this blog, we'll walk through setting up a basic MCP server using FastMCP, complete with a practical example to get you started.
What is FastMCP?
FastMCP is a Pythonic, high-level framework that abstracts the complexities of the MCP protocol, such as server setup, protocol handlers, and error management. It allows you to focus on building tools and resources for LLMs using simple Python functions and decorators.
What is MCP? The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a set of rules that lets AI models connect to external data and tools. Use MCP when you need your AI to:
- Fetch External Data: Query databases or APIs
- Run Custom Tools: Execute tasks you've programmed
- Enhance AI Capabilities: Combine AI with your systems for real-world results
Prerequisites
- Python 3.7+ installed
- A terminal (macOS/Linux) or PowerShell/CMD (Windows)
- Basic familiarity with Python and virtual environments
- (Optional) An MCP-compatible client like Claude Desktop or Cursor
Step 1: Install FastMCP
The recommended way to install FastMCP is using uv, a fast Python package manager:
# On macOS/Linux
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
# On Windows (PowerShell)
powershell -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"
After installing uv, create a project directory:
mkdir my-mcp-server
cd my-mcp-server
uv init
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate
Install FastMCP:
uv pip install "mcp[cli]"
Verify the installation:
fastmcp version
Step 2: Create a Simple MCP Server
Create a file named server.py:
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Initialize the MCP server with a name
mcp = FastMCP("CalculatorServer")
# Define a tool to add two numbers
@mcp.tool()
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers and return the result."""
return a + b
# Run the server
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport="stdio")
This code:
- Imports FastMCP from the MCP library
- Creates a server instance named "CalculatorServer"
- Defines a tool called
addusing the@mcp.tool()decorator - Runs the server using the stdio transport
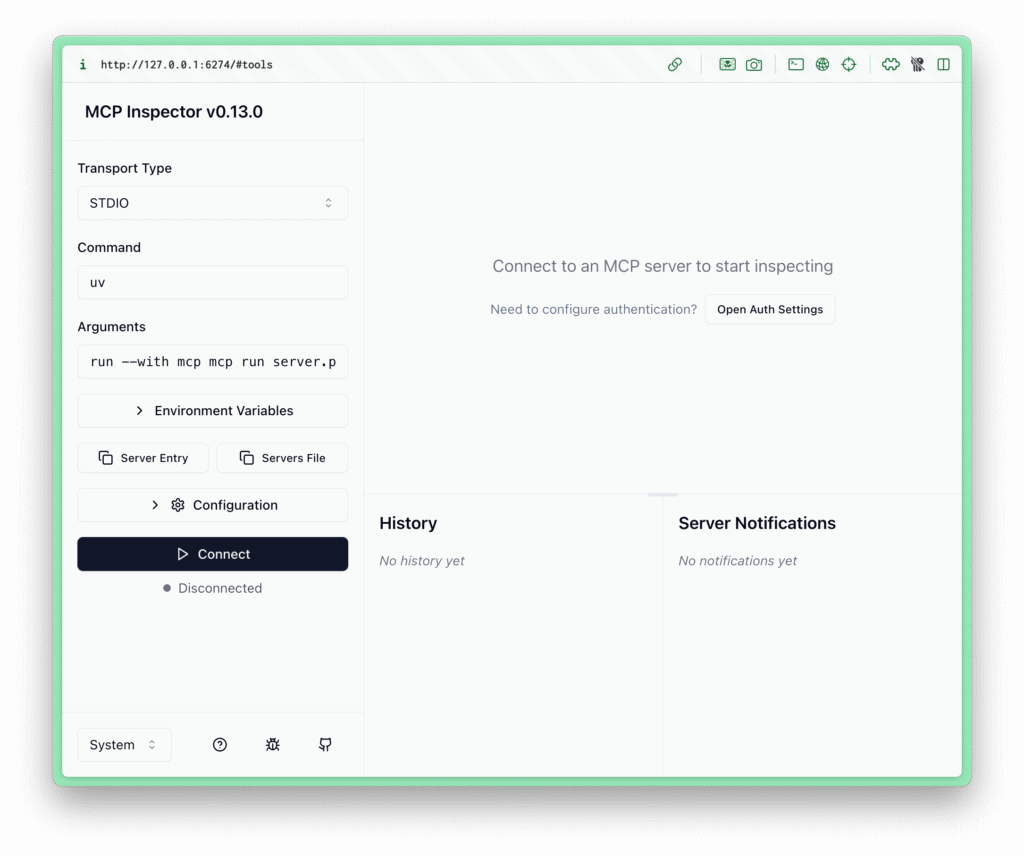
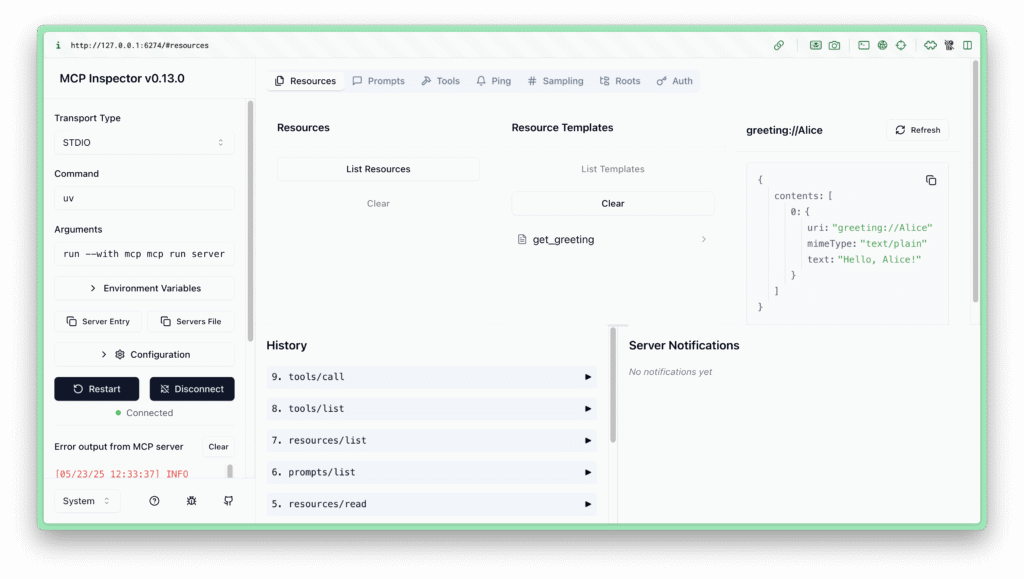
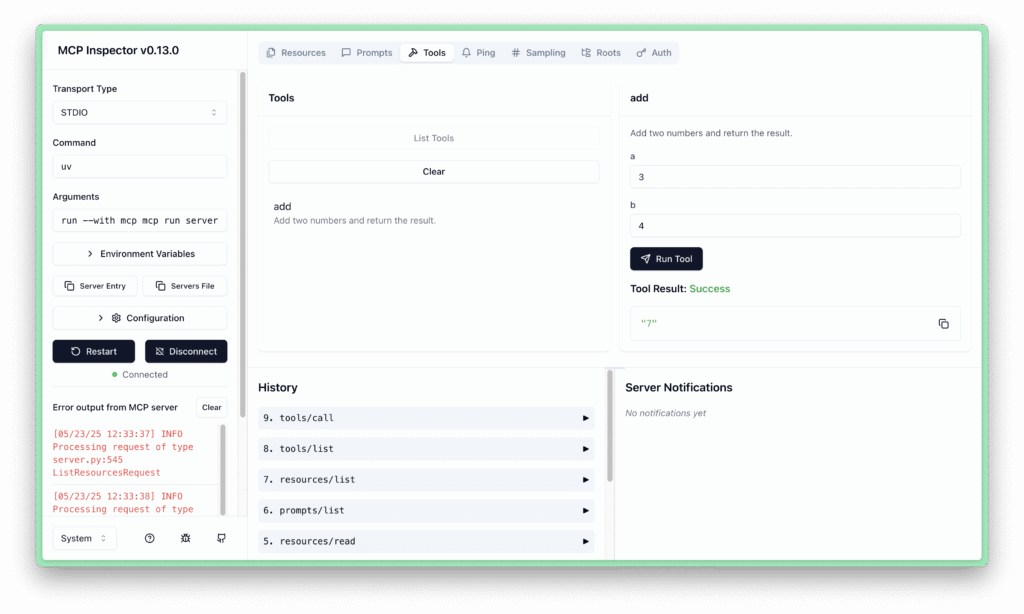
Step 3: Test the Server with MCP Inspector
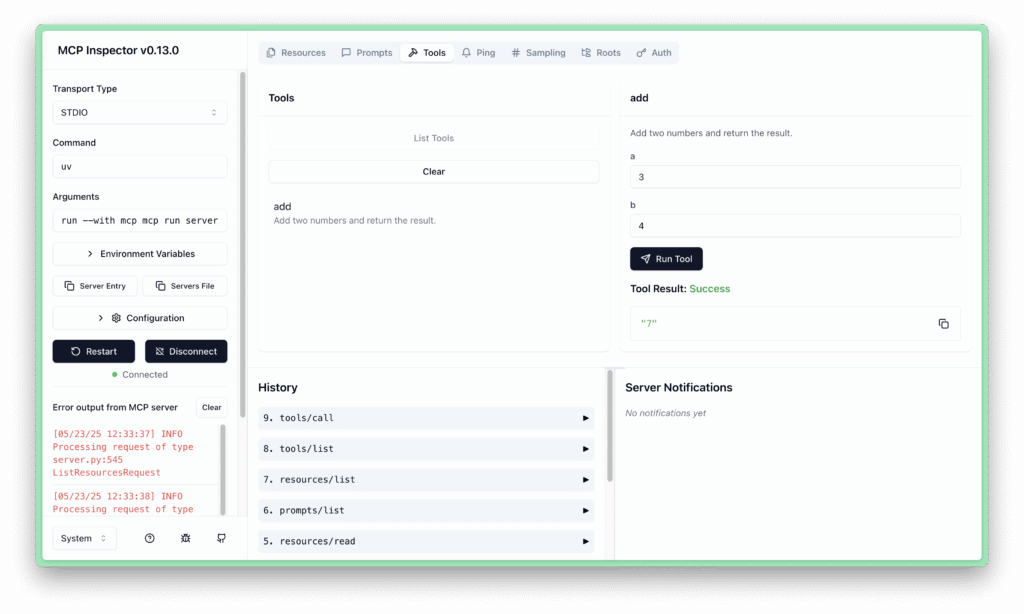
Start the server in development mode:
uv run mcp dev server.py
This launches the MCP Inspector in your browser (typically at http://127.0.0.1:6274).
- Click Connect to link to your server
- In the Tools tab, you'll see the
addtool listed - Enter values (e.g., a=4, b=3) and select Run Tool to test
Step 4: Integrate with an LLM Client (Optional)
To see your server in action with an LLM, integrate it with Cursor:
- Open your project directory in Cursor
- Go to File → Preferences → Cursor Settings → MCP → Add New Server
- Configure the server:
- Name: "Calculator"
- Type: Command
- Command:
uv run mcp run /path/to/your/server.py
- Save the configuration
- In Cursor's chat, type: "Add 5 and 3." The LLM should call your tool and return 8.
Step 5: Expand Your Server
Add more tools or resources. For example, a greeting resource:
# Add to server.py
@mcp.resource("greeting://{name}")
def get_greeting(name: str) -> str:
"""Return a personalized greeting."""
return f"Hello, {name}!"
Copy-and-Paste Example
Here's a complete, ready-to-run FastMCP server:
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Initialize the MCP server
mcp = FastMCP("MyFirstMCPServer")
# Define a tool to add two numbers
@mcp.tool()
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers and return the result."""
return a + b
# Define a resource for personalized greetings
@mcp.resource("greeting://{name}")
def get_greeting(name: str) -> str:
"""Return a personalized greeting."""
return f"Hello, {name}!"
# Run the server
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport="stdio")
How to Run:
- Save the code as
server.py - Ensure FastMCP is installed (
uv pip install "mcp[cli]") - Activate your virtual environment
- Run:
uv run mcp dev server.py - Open http://127.0.0.1:6274 to test
Why Use FastMCP?
- Minimal Boilerplate: Create tools and resources with just a few lines
- Pythonic Design: Uses decorators and type hints
- Powerful Features: Supports async functions, OpenAPI integration
- Debugging Tools: MCP Inspector makes testing straightforward
Next Steps
- Add more complex tools (APIs, databases)
- Deploy to AWS or Cloudflare
- Explore the FastMCP GitHub repository
Happy coding, and enjoy powering your LLMs with FastMCP!